Diagnosing PNH: Early identification and high-risk groups
Rapid recognition of the signs and symptoms of PNH and early diagnosis are important to patient management1,2
- The International Clinical Cytometry Society and International PNH Interest Group recommend testing high-risk patients.3-5
- Patients who meet the criteria within any of the high-risk groups for PNH should be tested for PNH with high-sensitivity flow cytometry with FLAER on peripheral blood, the standard diagnostic test for PNH.1,3,6,7
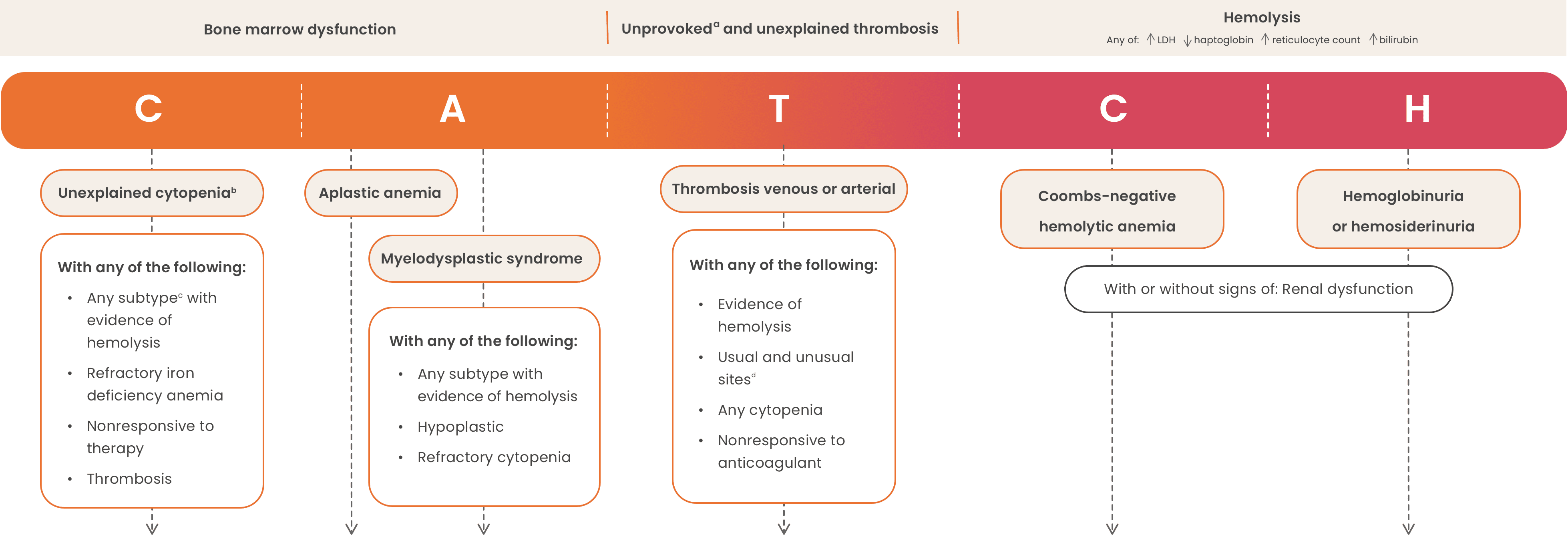
Use the CATCH algorithm to identify patients with PNH
Scroll through the CATCH algorithm to reveal PNH testing recommendations
Core signs and symptoms of PNH (any of the following)1,3,5,8,9
Symptoms of anemia
(eg, fatigue, tachycardia, shortness of breath, headache)
Thrombosis
Dark-colored urine
Intermittent abdominal pain
Esophageal spasms
Dysphagia
in association with 1 of the following or if the patient exhibits 1 of the following (in the absence of an above symptom)
High-risk groups associated with PNH1,3,5,8-10
This algorithm is intended as educational information for healthcare providers. It does not replace a healthcare provider’s professional judgment or clinical diagnosis.
aDeep vein thrombosis and/or pulmonary embolism in a patient with no antecedent major clinical risk factor for venous thromboembolism that is not provoked by surgery, trauma, immobilization, hormonal therapy (oral contraceptive or hormone replacement therapy), or active cancer.8
bUnexplained persistent cytopenia in a patient in whom (minimal) diagnostic criteria for myelodysplastic syndrome are not fulfilled.8
cAnemia, neutropenia, or thrombocytopenia.11
dUnusual sites include hepatic veins (Budd-Chiari syndrome), other intra-abdominal veins (portal, splenic, splanchnic), cerebral sinuses, and dermal veins.8
eDetects PNH cells down to a 0.01% clone size.1
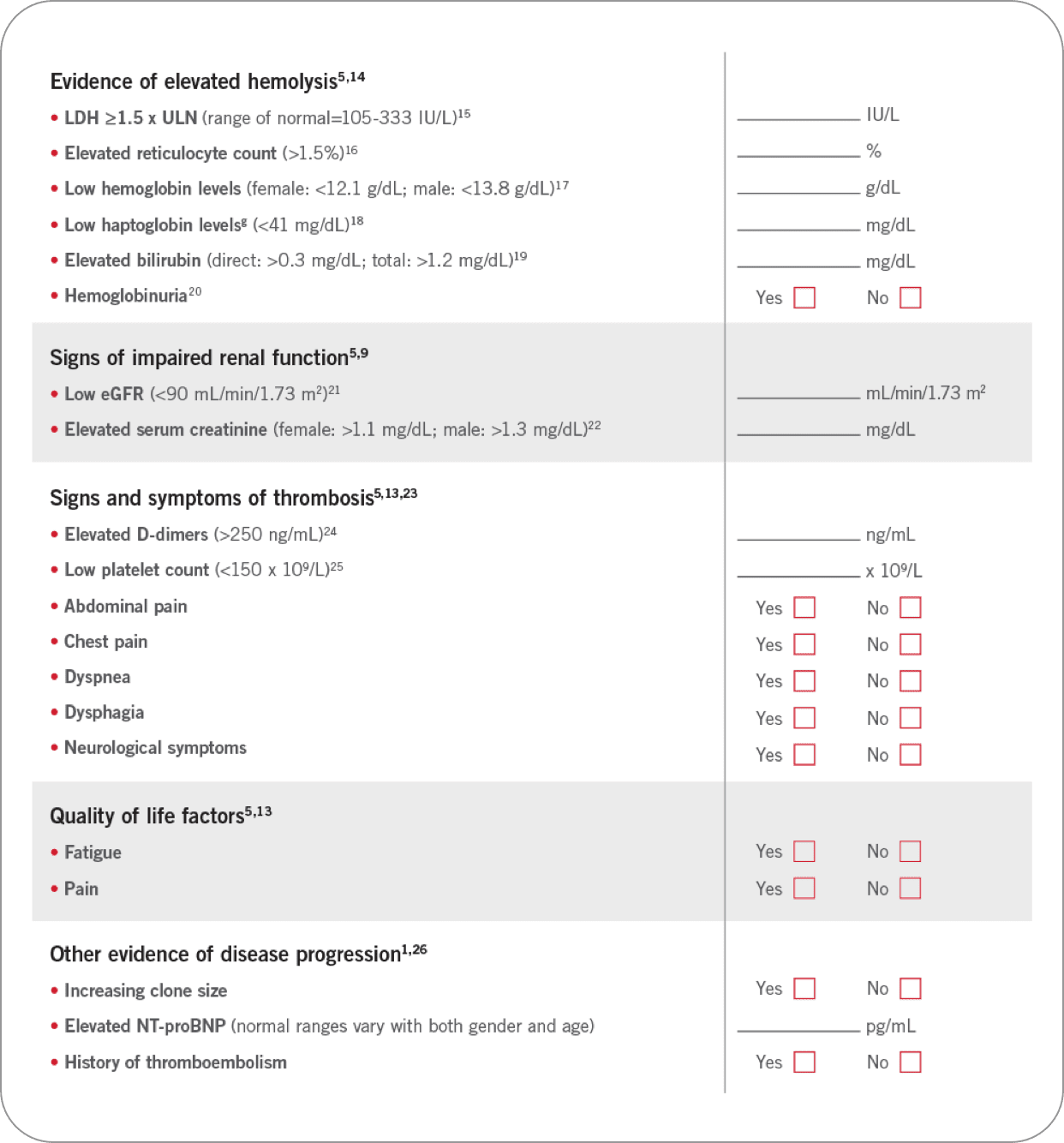
Comprehensive and routine clinical assessment is critical in identifying patients with PNH at risk of morbidities and early mortality3,5,12,13
In addition to looking at outward symptoms, use lab values to help determine the risk for your patient with PNH for serious morbidities and premature mortality.
Use this assessment tool to evaluate your patients for PNH
Has your patient presented with any of the following laboratory values or symptoms?f
fNormal laboratory values may vary slightly among different laboratories and also among individuals. Elevated values for this chart were defined by the upper limit, and low levels by the lower limit, of normal ranges identified by either MedlinePlus, Medscape, or the Mayo Foundation.
gLow haptoglobin is indicative of excess plasma hemoglobin released from hemolyzed red blood cells.27
- Borowitz MJ, et al. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2010;78(4):211-230.
- Richards SJ, Barnett D. Clin Lab Med. 2007;27(3):577-590, vii.
- Parker C, et al. Blood. 2005;106(12):3699-3709.
- Sutherland DR, et al. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2018;94(1):23-48.
- Sahin F, et al. Am J Blood Res. 2016;6(2):19-27.
- Dezern AE, Borowitz MJ. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2018;94(1):16-22.
- Brodsky RA. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 7th ed. Elsevier; 2018:415-424.
- Röth A, et al. Eur J Haematol. 2018;101(1):3-11.
- Hillmen P, et al. Am J Hematol. 2010;85(8):553-559.
- Patriquin CJ, et al. Eur J Haematol. 2019;102(1):36-52.
- Seidel MG. Blood. 2014;124(15):2337-2344.
- Hill A, et al. Br J Haematol. 2010;149(3):414-425.
- Weitz I, et al. Intern Med J. 2013;43(3):298-307.
- Brodsky RA. Blood. 2009;113(26):6522-6527.
- Lactate dehydrogenase test. MedlinePlus. Published February 6, 2020. Updated April 1, 2022. Accessed April 8, 2022. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003471.htm
- Reticulocyte count and reticulocyte hemoglobin content. Medscape. Updated September 5, 2014. Accessed April 8, 2022.https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2086146-overview
- Hemoglobin. MedlinePlus. Published January 13, 2020. Updated April 1, 2022. Accessed April 8, 2022. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003645.htm
- Haptoglobin blood test. MedlinePlus. Published February 6, 2020. Updated April 1, 2022. Accessed April 8, 2022. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003634.htm
- Bilirubin blood test. MedlinePlus. Published January 24, 2020. Updated April 1, 2022. Accessed April 8, 2022.https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003479.htm
- Hill A, et al. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17028.
- Glomerular filtration rate. MedlinePlus. Published July 7, 2019. Updated April 1, 2022. Accessed April 8, 2022.https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007305.htm
- Creatinine blood test. MedlinePlus. Published July 4, 2019. Updated April 1, 2022. Accessed April 8, 2022. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003475.htm
- Hill A, et al. Blood. 2013;121(25):4985-4996.
- D-dimer. Medscape. Updated February 22, 2022. Accessed April 8, 2022. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2085111-overview
- Platelet count. MedlinePlus. Published January 19, 2021. Updated April 1, 2022. Accessed April 8, 2022. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003647.htm
- Hill A, et al. Br J Haematol. 2012;158(3):409-414.
- Barcellini W, Fattizzo B. Dis Markers. 2015;2015:635670.
- Morado M, et al. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2017;92(5):361-370.