PNH case studies reveal hemolysis-related complications
Take a closer look at how assessing lab values and symptoms can indicate underlying, potentially life-threatening complications, including hemolysis, renal impairment, thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism
The following patients underwent more extensive tests when their lab signs and common symptoms indicated the possibility of PNH-related morbidities.
Tap on their test results to find out what underlying and potentially life-threatening complication was revealed.
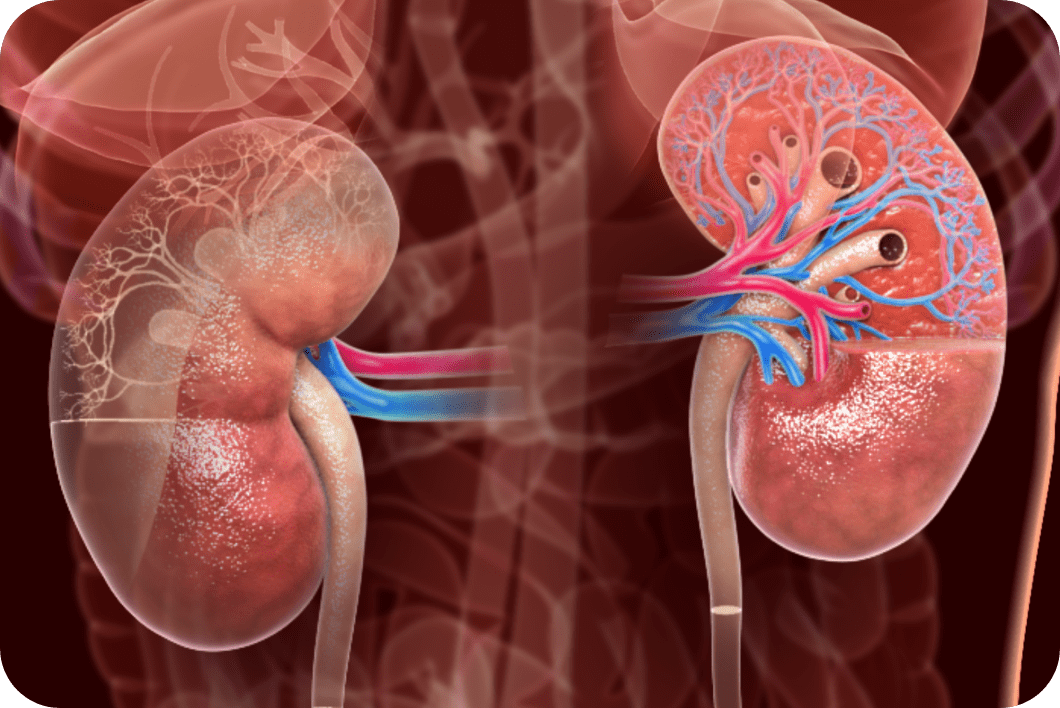
Patient with elevated sCr1
Renal impairment1
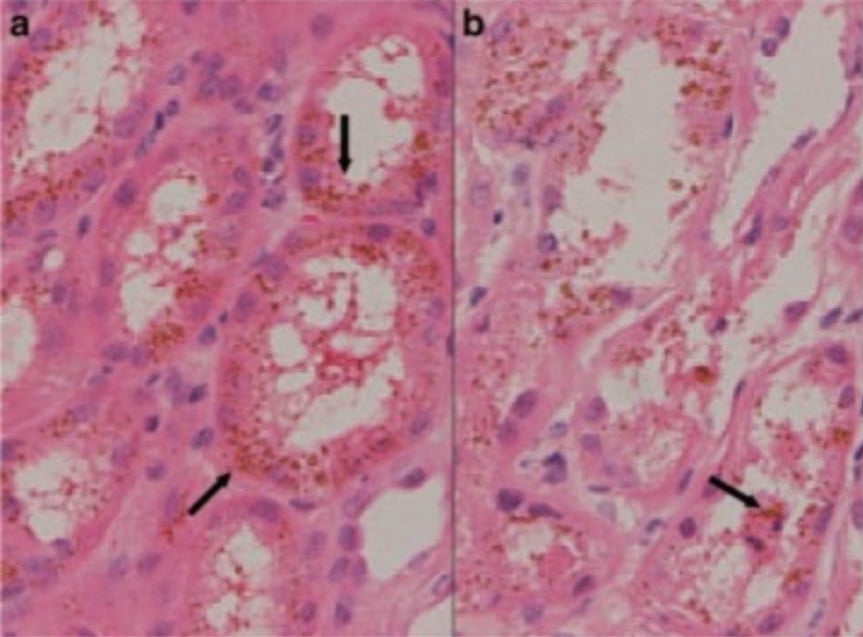
From Tsai CW, et al. Kidney Int. 2007;71(11):1187.
© 2007 International Society of Nephrology.
Biopsy results
A renal biopsy of the patient, following diagnosis, revealed extensive kidney damage and hemosiderin accumulation associated with high LDH and low haptoglobin indicative of intravascular hemolysis. (a) Pigment deposits.* (b) Tubular necrosis and degeneration.
*Arrows indicate pigment deposits.

Female, age 30
Hemoglobinuria
- Presence of red blood cells in urine under microscope
Renal impairment
- Elevated creatinine: 4.0 mg/dL (female: 0.6-1.1 mg/dL)
Signs of hemolysis
- Elevated LDH: 2454 IU/L (105-333 IU/L)
- Indirect hyperbilirubinemia: total/direct bilirubin, 3.01/0.71 mg/dL (total, 0.3 to 1.2 mg/dL; direct, 0 to 0.3 mg/dL)
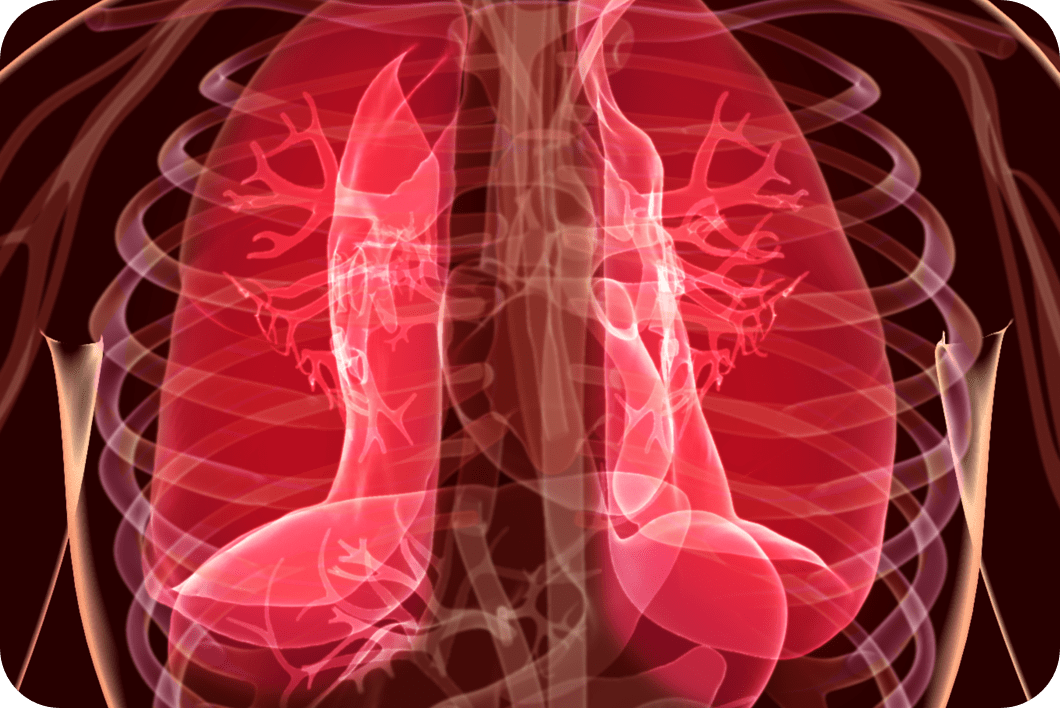
Patient (group) with dyspnea2
Pulmonary embolisms2
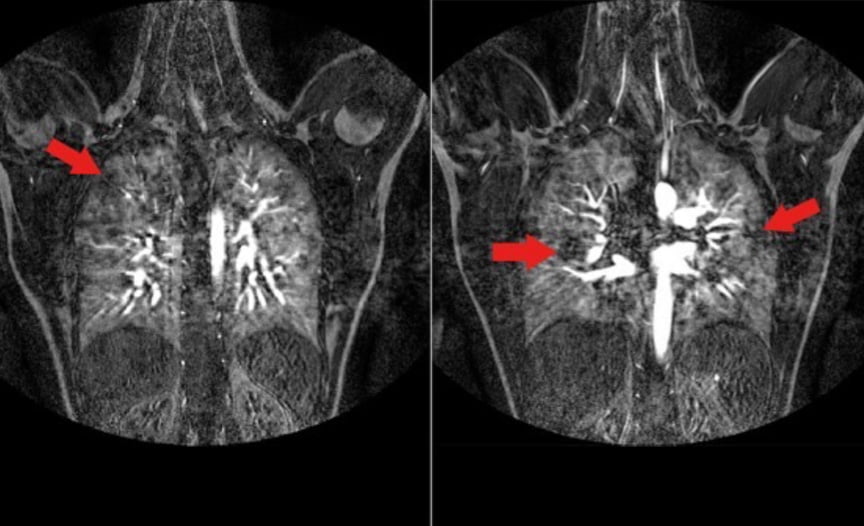
From Hill A, et al. Br J Haematol. 2012;158(3):409-414.
©2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd
MRI results
Six out of 10 patients were observed to have subclinical small pulmonary emboli recognized by MRI.
Imaging shows multiple perfusion defects in the posterior aspects of the lungs of a patient with PNH.*
- Patients had no reported clinical evidence of thrombosis in their medical history

10 patients (median age of 31.5 years)
Lab values from patients with PNH showed:
- Elevated LDH
- Elevated NT-proBNP
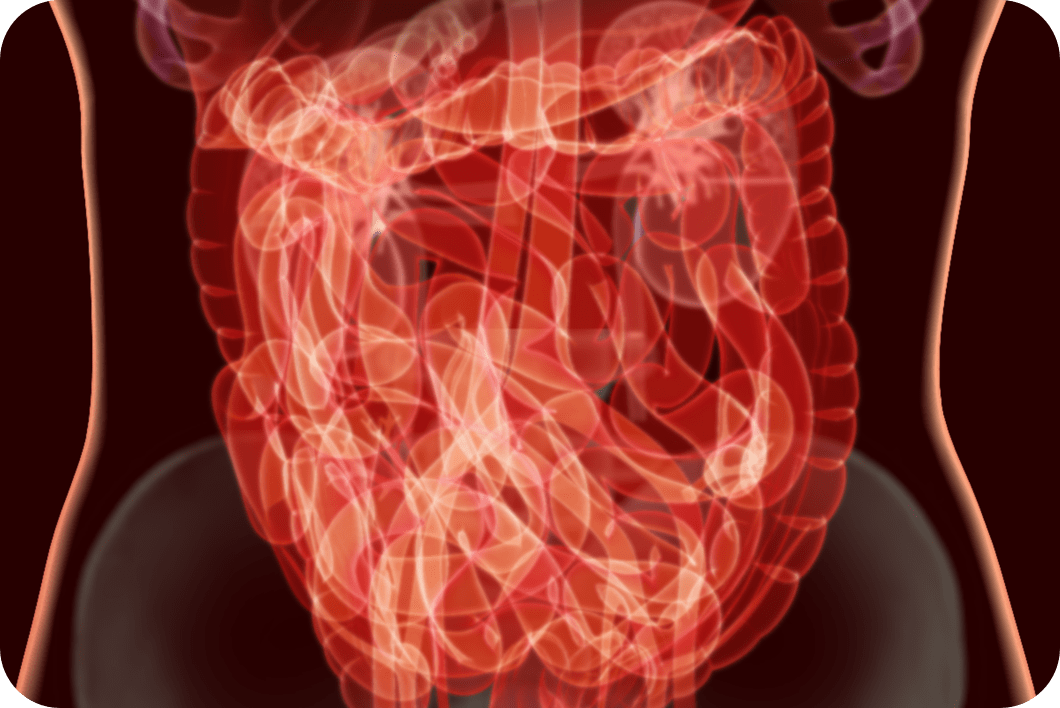
Patient with abdominal pain3
Thromboembolism3
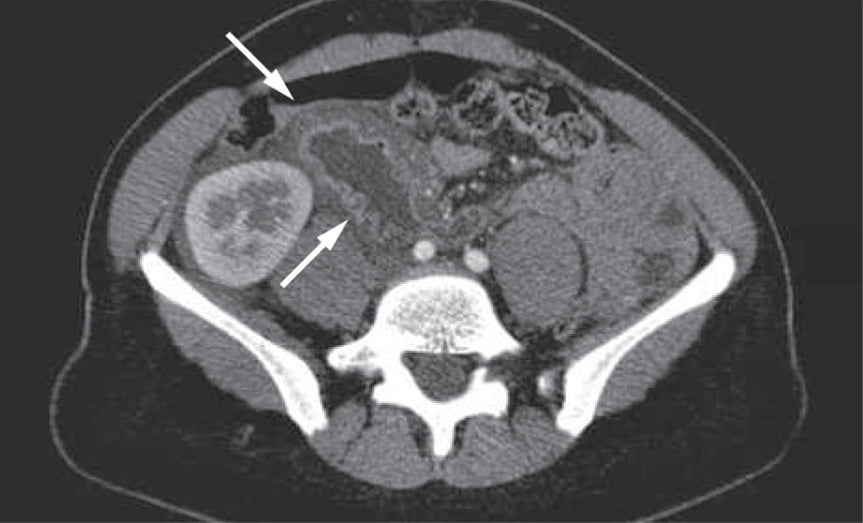
From Torres J, et al. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;7(7):410-414.
© 2010 Macmillan Publishers Limited.
CT scan results
Abdominal CT scan of the case patient at admission. The scan shows parietal thickening of the second portion of the duodenum (arrows).
- No arterial or venous thromboses were seen on angiographic CT examination

Female, age 33
Patient with PNH presented with lab values and symptoms including:
- Elevated LDH
- Elevated total bilirubin
- Low hemoglobin
- Abdominal pain
- Tsai CW, et al. Kidney Int. 2007;71(11):1187.
- Hill A, et al. Br J Haematol. 2012;158(3):409-414.
- Torres J, et al. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;7(7):410-414.